138. Copy List with Random Pointer
A linked list of length n is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer, which could point to any node in the list, or null.
Construct a deep copy of the list. The deep copy should consist of exactly n brand new nodes, where each new node has its value set to the value of its corresponding original node. Both the next and random pointer of the new nodes should point to new nodes in the copied list such that the pointers in the original list and copied list represent the same list state. None of the pointers in the new list should point to nodes in the original list.
For example, if there are two nodes X and Y in the original list, where X.random --> Y, then for the corresponding two nodes x and y in the copied list, x.random --> y.
Return the head of the copied linked list.
The linked list is represented in the input/output as a list of n nodes. Each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
val: an integer representingNode.valrandom_index: the index of the node (range from0ton-1) that therandompointer points to, ornullif it does not point to any node.
Your code will only be given the head of the original linked list.
Example 1:

Example 2:

Example 3:

Solution:
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
Node dummy = new Node(-1);
Node cur = dummy;
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
// head, new
while(head != null){
if (!map.containsKey(head)){
map.put(head, new Node(head.val));
}
cur.next = map.get(head);
if (head.random != null){
if (map.containsKey(head.random)){
cur.next.random = map.get(head.random);
}else{
map.put(head.random, new Node(head.random.val));
cur.next.random = map.get(head.random);
}
}
cur = cur.next;
head = head.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
Node dummy = new Node(-1);
Node cur = dummy;
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
while(head != null){
if (!map.containsKey(head)){
map.put(head, new Node(head.val));
}
cur.next = map.get(head);
cur = cur.next;
if (head.random != null){
if (!map.containsKey(head.random)){
map.put(head.random, new Node(head.random.val));
}
cur.random = map.get(head.random);
}
head = head.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
// TC: O(n)
// SC: O(n)
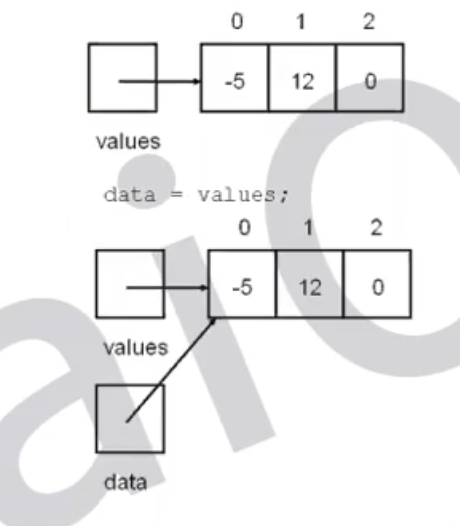
Shallow Copy vs Deep Copy
public class ShallowCopy{ private int[] value = {-5, 12, 0}; // ref of value = 0xFFFF0001 private int[] data; // makes a shallow copy of values; public ShallowCopy(int[] values){ data = values; // ref of data = value == 0xFFFF0001 } }
DeepCopy creates (= new) an array and copies over the values;
public class DeepCopy{ private int[] value = {-5, 12, 0}; // ref of value = 0xFFFF0001 private int[] data; // deep copy of values public DeepCopy(int[] values){ data = new int[values.length]; // ref of data = 0xFFFF0005 for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++){ data[i] = values[i]; } } }
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
// Method 1: using HashMap to avoid copy multiple times for the same node
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null){
return null;
}
// Sential ndoe to help construct the deep copy.
Node dummy = new Node(0); // value 0
Node cur = dummy;
// 0 -> 7 -> 13
// d
// c
// h
// head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
// Maintains the mapping between the node in the original list and
// the corresponding node in the new list
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
/*
Map: {7, [7]},{13,[13]} {}
*/
while (head != null){
// Copy the current node if necessary.
if (!map.containsKey(head)){
map.put(head, new Node(head.val));
}
// Connect the copied node to the deep copy list.
cur.next = map.get(head);
if (head.random != null){
if (!map.containsKey(head.random)){
map.put(head.random, new Node(head.random.val));
}
// Connect the copied node to the random pointer.
cur.next.random = map.get(head.random);
}
head = head.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
//TC: O(n)
//SC: O(n)
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
// 复制每个节点,把新节点直接插到原节点的后面
for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next.next) {
cur.next = new Node(cur.val, cur.next);
}
// 遍历交错链表中的原链表节点
for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next.next) {
if (cur.random != null) {
// 要复制的 random 是 cur.random 的下一个节点
cur.next.random = cur.random.next;
}
}
// 把交错链表分离成两个链表
Node newHead = head.next;
Node cur = head;
for (; cur.next.next != null; cur = cur.next) {
Node copy = cur.next;
cur.next = copy.next; // 恢复原节点的 next
copy.next = copy.next.next; // 设置新节点的 next
}
cur.next = null; // 恢复原节点的 next
return newHead;
}
}
// TC: O(n)
// SC: O(1)